Case Studies
Explore our confidential case studies where Xpert Forensics uncovered digital fraud, insider threats, data leaks, and cyber misconduct using advanced forensic tools and investigative techniques. Each case reflects our commitment to precision, discretion, and delivering actionable insights that drive resolution.
Chrome Browser Artifacts Analysis Using MAGNET AXIOM
Introduction
Google Chrome is one of the most widely used web browsers and is a rich source of digital evidence in both civil and criminal investigations. Chrome artifacts can reveal a user’s browsing behavior, search intent, social media activity, downloads, form inputs, and interaction timelines. In forensic investigations, it is often unnecessary and impractical to image an entire disk when the scope is limited to browser usage.
This article explains, in detail, how only Google Chrome artifacts can be selectively exported, examined, and analyzed using MAGNET AXIOM, specifically leveraging the “Export RAW Chrome Artifact Files” method. The workflow and findings are aligned with real-world forensic case studies suitable for expert reporting and courtroom presentation.
Why Selective Chrome Artifact Extraction?
Selective extraction is particularly useful when:
- The investigation scope is limited to internet activity or user intent
- Large disk sizes make full imaging time-consuming
- Legal authorization restricts acquisition to browser data only
- Rapid triage or preliminary analysis is required
Using MAGNET AXIOM’s RAW export capability ensures:
- Minimal data handling
- Reduced analysis time
- Preservation of original metadata
- Defensible forensic methodology
Chrome Artifact Storage Locations (Windows)
Chrome stores user data within the following directory: C:\Users\<Username>\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\
Key subfolders and files include: Profile Folders
- Default
- Profile 1, Profile 2, etc.
Each profile represents a separate Chrome user context.
Critical Chrome Artifact Files
Artifact | File Name | Forensic Value |
Browsing History | History | Visited URLs, timestamps |
Downloads | History | Download source & time |
Cookies | Cookies | Session & login artifacts |
Autofill | Web Data | Form & input values |
Saved Passwords | Login Data | Encrypted credentials |
Favicons | Favicons | Website interaction indicators |
Search Terms | History | User intent & keywords |
Important Note: Autofill data and saved passwords are stored in Web Data and Login Data SQLite databases within the Chrome User Data path. Passwords remain DPAPI-encrypted and require OS-level decryption support.
Step-by-Step: Exporting RAW Chrome Artifact Files Using MAGNET AXIOM
Step 1: Add Evidence Source
- Launch MAGNET AXIOM Process
- Add evidence source (disk image / physical drive/ selective raw data)
Step 2: Choose Targeted Artifact Processing
- Select Computer Evidence
- Enable Web & Browser Artifacts only
- Specifically select Google Chrome
Step 3: Use RAW Artifact Export Option
- Enable Export RAW Chrome Artifact Files
- AXIOM extracts original SQLite databases and related files
- Original file paths and timestamps are preserved
Step 4: Complete Processing
- AXIOM parses Chrome databases
- Results are loaded into AXIOM Examine for analysis
Analysis in MAGNET AXIOM Examine
AXIOM Examine categorizes Chrome data into structured artifacts for easier interpretation.
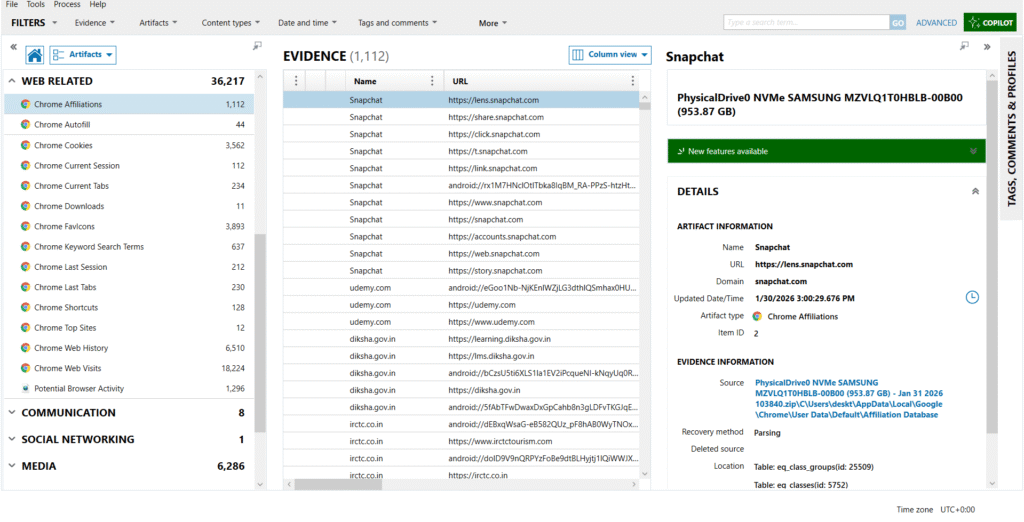
Web-Related Artifacts
The following Chrome artifacts were identified:
- Chrome Web History
- Chrome Web Visits
- Chrome Keyword Search Terms
- Chrome Downloads
- Chrome Cookies
- Chrome Favicons
Social Media & Platform Activity
Social Media URLs
AXIOM identified 2,764 Social Media URLs, derived primarily from Chrome Favicons and History artifacts.
Platforms observed:
- YouTube – video watches, channel access, studio access
- LinkedIn – profile views, feed access, analytics pages
- Instagram – profile visits and CDN resource access
- Facebook – URL references
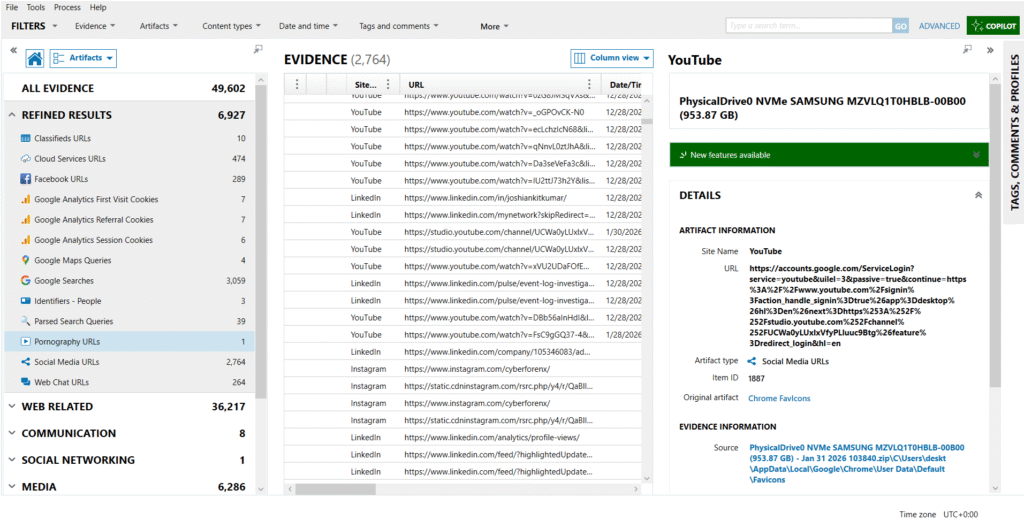
Each artifact includes:
- Site name
- Full URL
- Date and time (UTC)
- Source artifact (e.g., Chrome Favicons)
- Original file path
Example Forensic Interpretation
- Repeated YouTube URLs indicate video consumption patterns and potential content interest
- LinkedIn analytics and profile URLs suggest professional or recruitment-related activity
- Instagram profile URLs confirm user-initiated profile access
These findings are crucial in:
- Behavioral analysis
- Timeline reconstruction
- Establishing user intent
Chrome Favicons – Hidden but Powerful Evidence
Favicons are small website icons stored locally by Chrome. Although often overlooked, they are forensically significant.
Why Favicons Matter:
- Persist even when history is partially cleared
- Indicate website interaction
- Correlate with visited domains
AXIOM correlates Favicons with:
- URLs
- Browser sessions
- Social media platforms
In this case, Chrome Favicons served as the original artifact for multiple Social Media URL findings.
Autofill & Password Artifacts
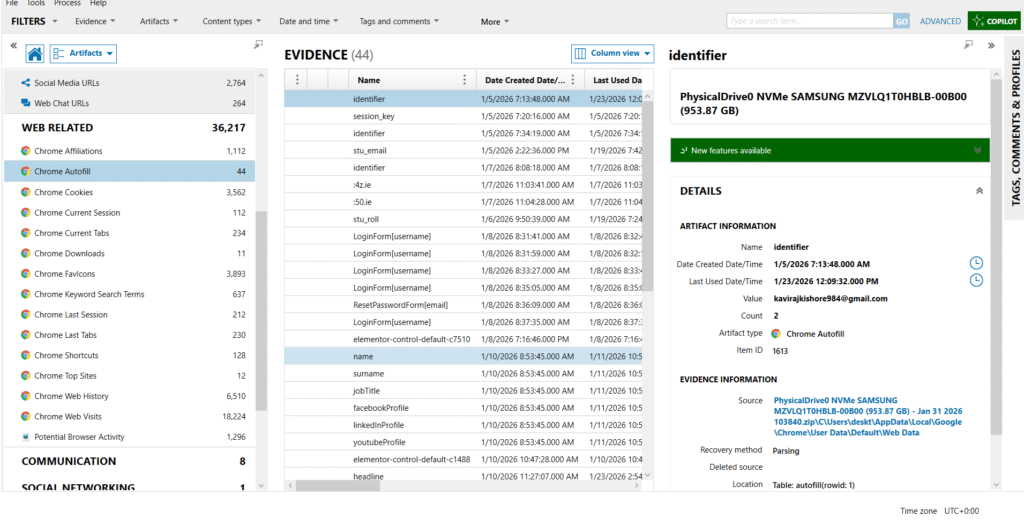
Autofill Data
Stored in: Web Data
Includes:
- Names
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Form input values
Saved Passwords
Stored in: Login Data
- Encrypted using Windows DPAPI
- AXIOM decrypts passwords when system credentials are available
These artifacts are valuable for:
- Account attribution
- Linking user to online services
Timeline Correlation & Evidential Value
By correlating:
- Web Visits
- Social Media URLs
- Search Terms
- Favicons
- Download artifacts
Investigators can:
- Establish which websites a user actually visited
- Determine when and how frequently those websites were accessed
- Reconstruct accurate activity timelines
- Support or refute statements made by the user
Browser artifacts provide objective, system-generated records of user activity. Unlike verbal statements or assumptions, these artifacts allow investigators to identify the factual truth about a user’s online behavior, including specific website visits, platform usage, and interaction patterns.
Cyber Attack & Intrusion Perspective
In cyber attack investigations, browser artifacts are crucial for identifying whether an attacker downloaded tools, payloads, or malicious files to gain unauthorized access or bypass system security. Chrome download records, visited exploit-related URLs, and search terms may reveal:
- Download of malware, scripts, or exploit kits
- Access to phishing, command-and-control, or dropper websites
- Attempts to bypass security controls or escalate privileges
Such evidence helps determine initial access vectors, attacker intent, and whether the compromise originated from user-driven activity or external intrusion.
User Behavior & Session-Level Understanding
From a forensic investigation perspective, browser artifacts also allow investigators to determine:
- Which browser sessions were active
- Which websites were accessed during each session
- The sequence and continuity of user activity across sessions
By analyzing session artifacts (Current/Last Session, Tabs) along with history and visit records, an examiner can gain contextual knowledge about the user, including browsing habits, interests, intent, and behavior patterns. This understanding helps investigators form a clearer picture of how and why the user interacted with specific websites.
When multiple artifacts (history, downloads, favicons, cookies, searches, sessions) independently point to the same activity, the findings become highly reliable and evidentially strong, suitable for expert reporting and court presentation.
Conclusion
Selective extraction and analysis of Google Chrome artifacts using Export RAW Chrome Artifact Files method is a powerful and efficient forensic approach. Even without full disk imaging, investigators can reconstruct browsing behavior, social media interactions, and user intent with high evidential value.
How Xpert Forensics Can Help
At Xpert Forensics, we specialize in uncovering hidden digital trails. Our certified forensic investigators use industry-leading tools and methodologies to ensure that every byte of evidence is discovered, validated, and reported.
Need expert digital forensic support or training?
📩 Feel free to connect with us today. | Email: service@xpertforensics.in

The article explains Chrome browser artifact analysis in a clear and practical way. Using MAGNET AXIOM makes the topic feel very relevant to real forensic investigations, not just theory.
The flow of the article is smooth, and the screenshots help in understanding the tool’s output. A bit more explanation for each image would make it even clearer for readers.
The discussion of artifacts such as browsing history, cookies, and cached data is useful and well explained. Adding some real-world challenges or limitations faced during the analysis would make the article stronger.